Are Wrist Blood Pressure Meters Accuracy
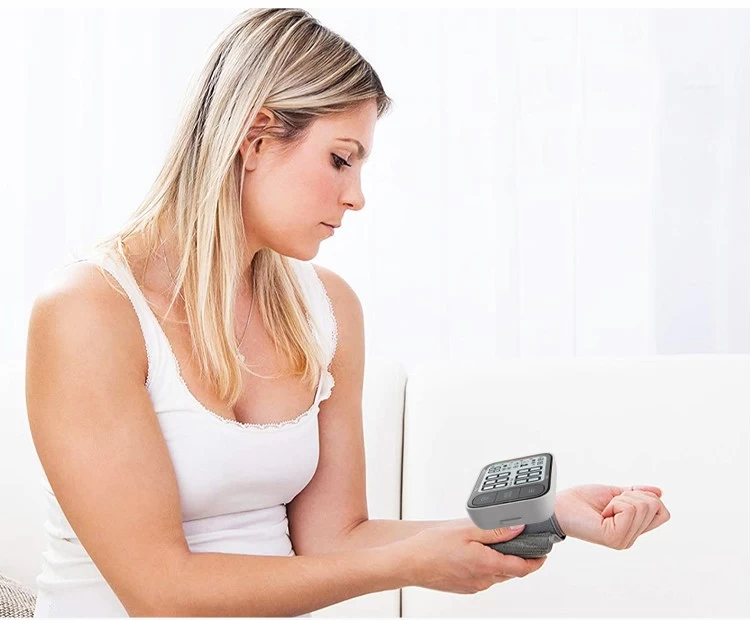
How to Use a Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor

[Wrist blood pressure monitors offer portability and convenience compared to traditional upper-arm devices, but their accuracy depends heavily on proper technique.]
Monitoring blood pressure at home is essential for managing hypertension, tracking cardiovascular health, or simply staying informed about your well-being. Wrist blood pressure monitors offer portability and convenience compared to traditional upper-arm devices, but their accuracy depends heavily on proper technique. This guide will walk you through using a wrist monitor correctly, interpreting results, and avoiding common pitfalls.
Table of Contents:
1.Understanding Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors
2.Pre-Measurement Preparation
3.Step-by-Step Measurement Process
4.Common Mistakes to Avoid
5.Interpreting Your Readings
6.When to Choose a Wrist Monitor
7.Maintenance Tips
8.Frequently Asked Questions
9.Conclusion
1.Understanding Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors
How They Work
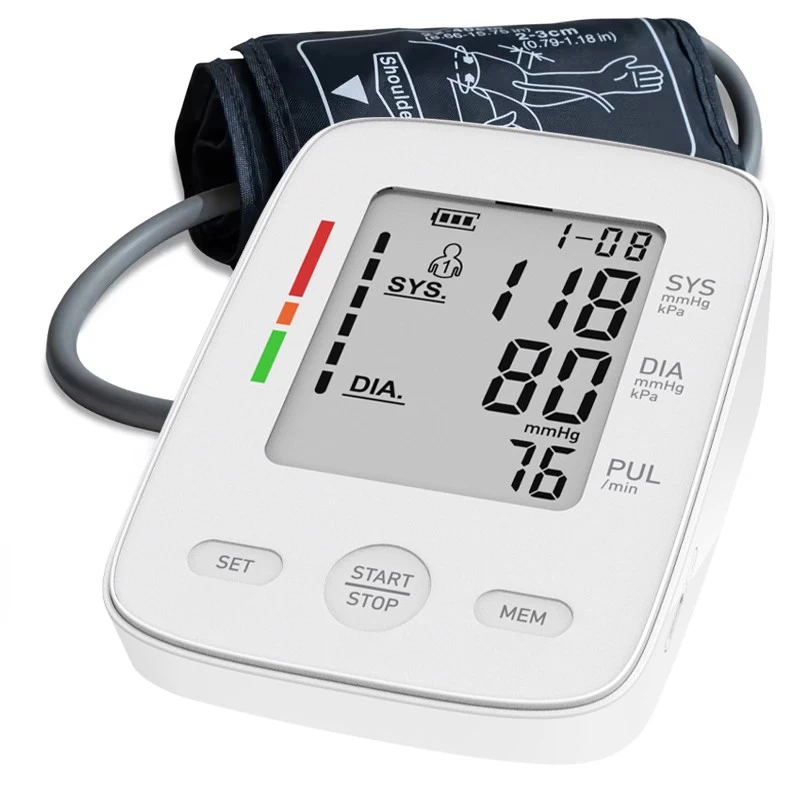
Wrist monitors use oscillometric technology to detect blood flow vibrations in the radial artery. A sensor in the cuff converts these vibrations into systolic (pressure during heartbeats) and diastolic (pressure between beats) readings.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Compact, easy to self-administer, ideal for travel.
- Cons: Sensitive to positioning errors; readings may vary more than upper-arm devices.

[do wrist blood pressure monitors work photo]
2.Pre-Measurement Preparation
1. Choose a Reliable Device
- Opt for models validated by medical organizations (e.g., FDA-approved, ESH-certified).
- Check user reviews for consistency and ease of use.
2. Avoid Influencing Factors
- 30 Minutes Before:
- Avoid caffeine, nicotine, exercise, or heavy meals.
- Empty your bladder.
- 5 Minutes Before:
- Sit quietly in a chair with back support.
- Relax your arm and avoid talking.
3. Positioning Matters
- Remove tight clothing or accessories from your wrist.
- Place the monitor on your non-dominant wrist (unless instructed otherwise by your doctor).
Do wrist blood pressure monitors work
[Wrist BP Machine Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors Factory Video]
3.Step-by-Step Measurement Process
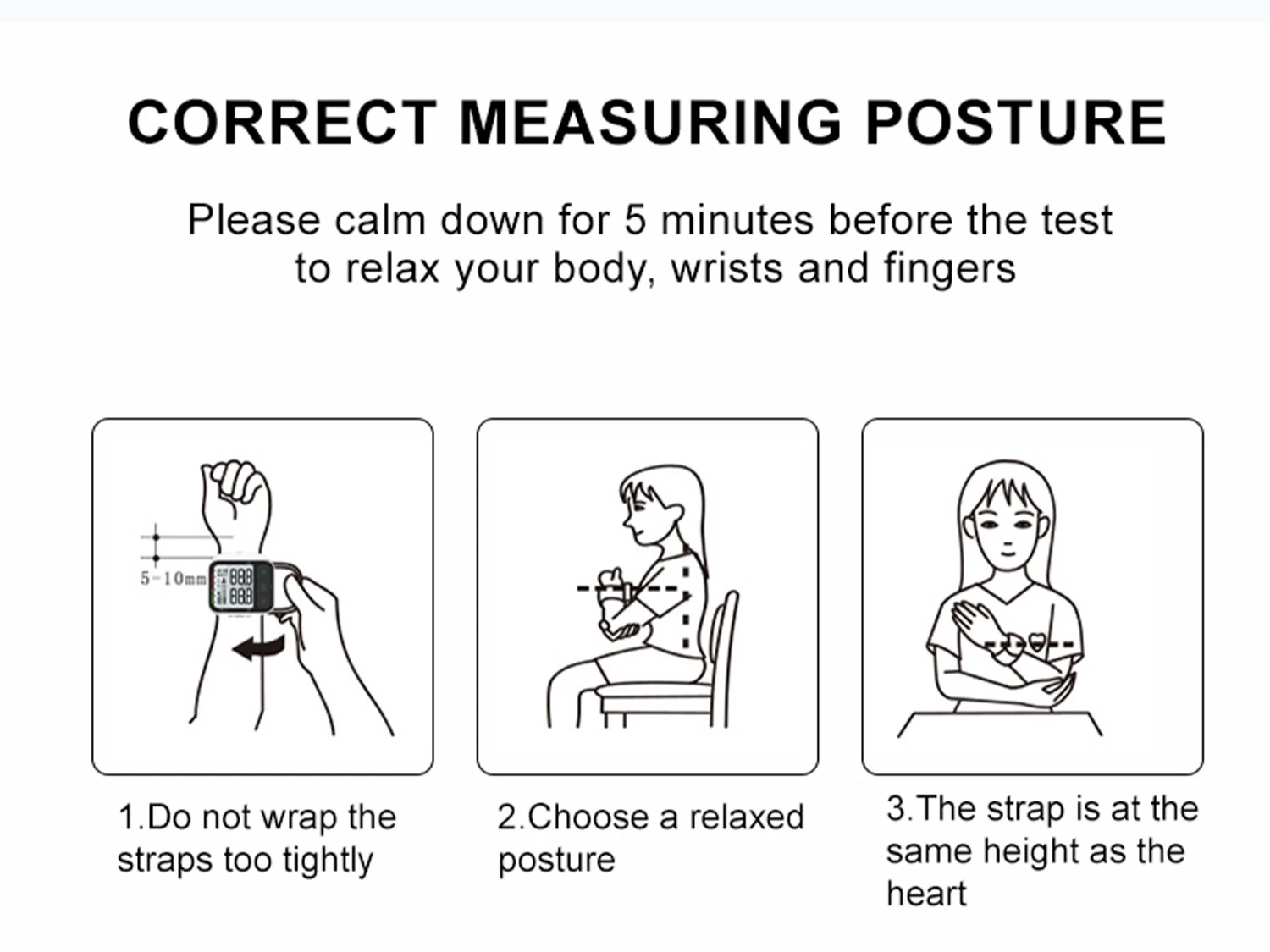
Step 1: Proper Posture
- Sit upright with feet flat on the floor.
- Rest your elbow on a table so your wrist is at heart level.
Critical Tip: If your wrist is above/below heart level, readings may be inaccurate by up to 10 mmHg.
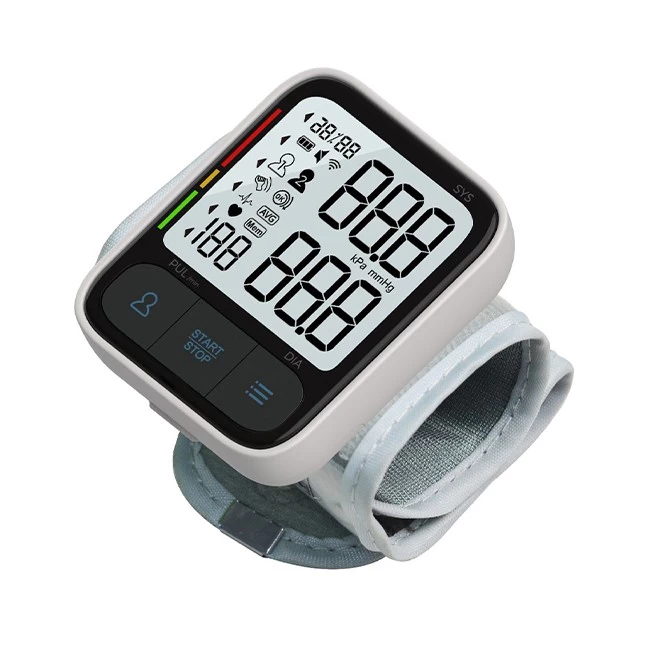
Step 2: Apply the Cuff Correctly
- Wrap the cuff snugly around your bare wrist:
- Position the monitor 1-2 cm (0.5 inches) above the wrist crease.
- Ensure the display faces inward, toward your palm.
- Fasten the cuff so it’s tight enough to stay in place but doesn’t restrict circulation.
Step 3: Initiate the Reading
- Press the "Start" button. The cuff will inflate automatically.
- Keep your arm relaxed and still during inflation. Avoid bending your wrist or fingers.
- Wait for deflation. The device will display your systolic/diastolic pressures and pulse rate.
Step 4: Record the Results
- Note readings in a logbook or app. Many devices store past measurements internally.
- Take 2-3 readings 1–2 minutes apart and average them for better accuracy.
[Do wrist blood pressure cuffs work]
4.Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Incorrect Wrist Height
- Why it matters: A wrist positioned too high/low creates hydrostatic pressure errors.
- Fix: Use a pillow or stack of books to elevate your arm to heart level if needed.
2. Cuff Misplacement
- Placing the cuff too loose, tight, or over clothing skews results.
3. Movement or Talking
- Even slight muscle contractions can raise systolic pressure by 5–10 mmHg.
4. Ignoring Calibration
- Validate your device’s accuracy annually at a clinic or pharmacy.
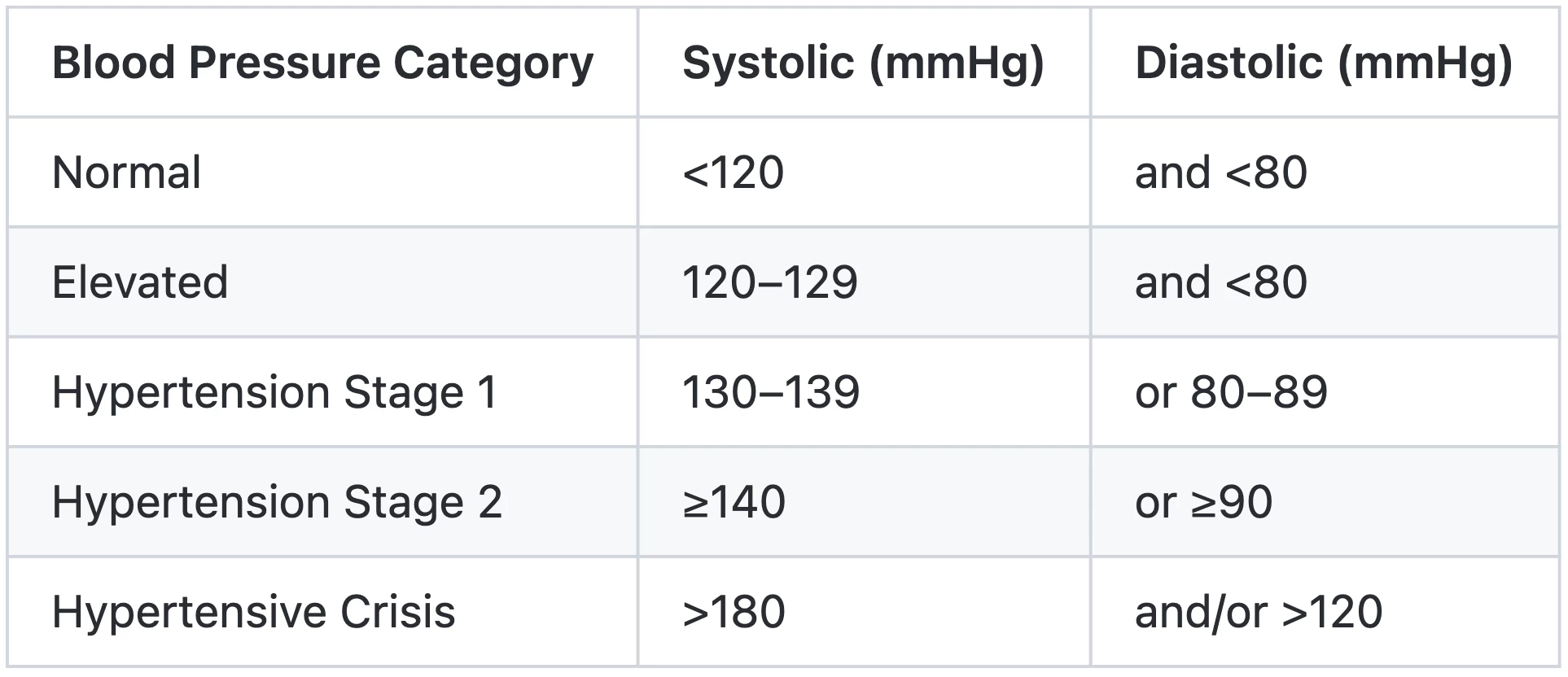
5.Interpreting Your Readings
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | <120 | and <80 |
| Elevated | 120–129 | and <80 |
| Hypertension Stage 1 | 130–139 | or 80–89 |
| Hypertension Stage 2 | ≥140 | or ≥90 |
| Hypertensive Crisis | >180 | and/or >120 |
- Action Steps:
- Normal/Elevated: Continue monitoring monthly.
- Stage 1/2: Consult a doctor for lifestyle changes or medication.
- Crisis Range: Seek immediate medical attention.
6.When to Choose a Wrist Monitor
Ideal For:
- Frequent travelers.
- Individuals with limited mobility or large upper arms.
- Those who find upper-arm cuffs uncomfortable.
Not Recommended For:
- People with arrhythmias or arterial stiffness (may require professional-grade devices).
- First-time users without guidance from a healthcare provider.
7.Maintenance Tips
- Battery Care: Replace batteries promptly when low; erratic power can affect sensors.
- Cuff Hygiene: Wipe the cuff with a damp cloth; avoid submerging it in water.
- Storage: Keep the device in a dry, temperature-stable environment.
8.Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are wrist monitors as accurate as upper-arm models?
Q: Wrist blood pressure monitor vs arm blood pressure monitor?
Q: Wrist bp monitor vs arm bp monitor?
A: They can be if used correctly, but arm monitors are generally more reliable for clinical use.
Q: Why do my readings fluctuate throughout the day?
A: Blood pressure naturally varies with stress, activity, and circadian rhythms. Measure at consistent times (e.g., morning/evening).
Q: Can I use a wrist monitor if I have obesity?
A: Yes, but ensure the cuff fits properly. Some brands offer extended-size cuffs.
9.Conclusion
Wrist blood pressure monitors empower users to track their health proactively but demand strict adherence to technique. Always cross-check unusual readings with a healthcare provider’s equipment. Pair regular monitoring with heart-healthy habits—balanced diet, exercise, and stress management—for optimal results.