Which Arm Is More Accurate for Blood Pressure?
When it comes to determining which arm is more accurate for blood pressure measurement, it depends on various factors. Usually, there is no significant difference between the two arms in healthy individuals. However, in cases of certain conditions like vascular disorders, the accuracy might vary. It's best to establish a baseline using the preferred arm and monitor consistently for reliable results.
Table of Contents
1.Introduction to Blood Pressure Measurement
3.Medical Guidelines on Arm Preference
4.Factors Influencing Blood Pressure Readings
5.How to Measure Blood Pressure Correctly
6.Common Questions and Myths Debunked
1. Introduction to Blood Pressure Measurement
Blood pressure (BP) measurement is a critical diagnostic tool for assessing cardiovascular health. Accurate readings are essential for diagnosing hypertension, guiding treatment, and preventing complications such as stroke or heart disease. Traditional cuff-based methods, oscillometric devices, and newer technologies like photoplethysmography (PPG) have been developed to improve accuracy and convenience. However, even with advanced algorithms and wearable devices, proper technique—including arm selection—plays a pivotal role in ensuring reliable results.
Did you know your blood pressure (BP) can differ between arms? Studies show a 5-10 mmHg variance is common, but consistent differences >10 mmHg may signal vascular issues. For accuracy:
1. Check both arms first: Measure BP in both arms during your initial reading. Use the arm with the higher value for future checks.
2. Right vs. left: While right-arm readings are often default (closer to the heart), left-arm use is fine if no major difference exists.
3.Consistency matters: Stick to one arm for tracking trends over time.
4.Seek advice if the difference exceeds 15 mmHg—it could indicate artery blockages or other conditions.
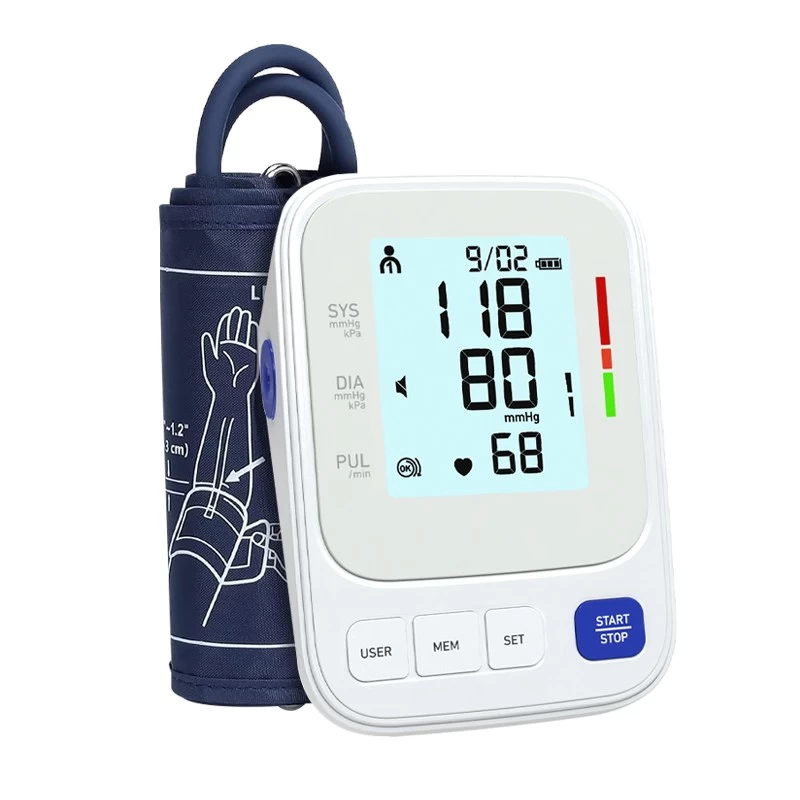
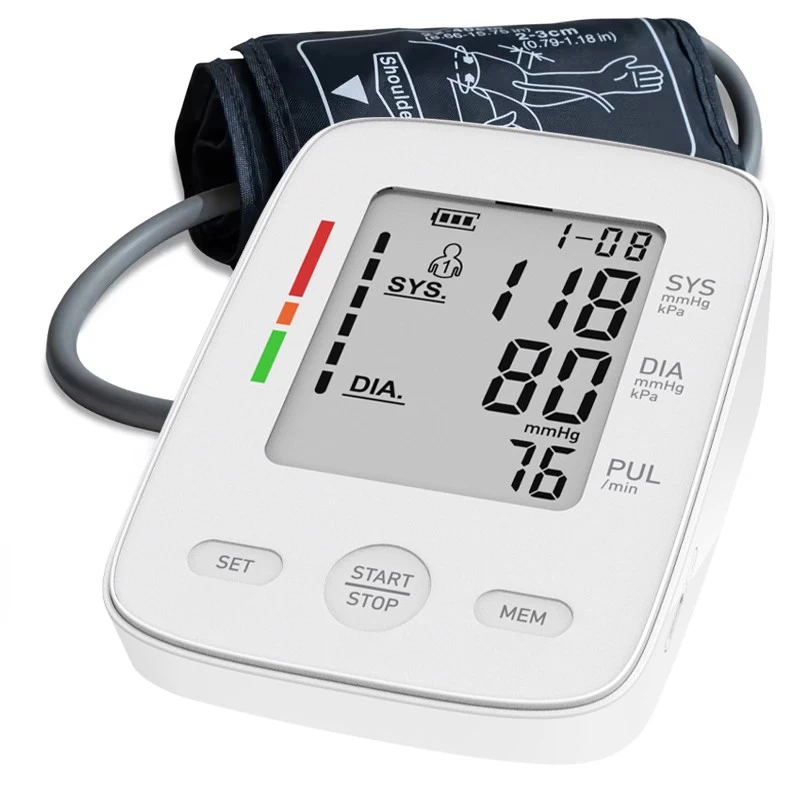
Always measure while seated, rested, and with a validated blood pressure monitor. To ensure health safety and accurate readings Finicare Medical FC-BP25 Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitor is one of the best solutions. The device is known for its compactness and accuracy and is recommended by many doctors and health practitioners. Finicare Medical FC-BP25 is the best option out there.

2. Why Arm Selection Matters
The choice of arm for BP measurement can significantly affect readings due to anatomical and physiological differences:
- Anatomical Variations: The left arm is closer to the heart, but the right subclavian artery may branch differently, leading to slight pressure discrepancies.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like atherosclerosis or arterial stenosis in one arm can cause persistently higher readings.
- Consistency: Using the same arm for repeated measurements reduces variability and improves tracking accuracy.
Studies suggest that inter-arm differences (IADs) exceeding 10 mmHg systolic may indicate cardiovascular risks, warranting further evaluation.
3. Medical Guidelines on Arm Preference
Leading health organizations provide specific recommendations:
- Initial Measurement: Measure both arms during the first assessment. The arm with the higher reading should be used for future monitoring.
- Chronic Conditions: For patients with known vascular diseases, the arm with consistently higher readings is preferred.
- Device Calibration: Oscillometric devices often require validation for specific arms due to algorithm dependencies.
4. Factors Influencing Blood Pressure Readings
Beyond arm selection, multiple factors affect accuracy:
- Cuff Size: A misfitting cuff can over- or underestimate BP by up to 20 mmHg.
- Posture: Arm position at heart level is critical; elevation or lowering introduces errors.
- Movement and Stress: Physical activity or anxiety can transiently elevate readings.
- Technology: Advanced methods like continuous wavelet transform (CWT) in PPG-based systems improve signal processing but require standardized protocols.
5. How to Measure Blood Pressure Correctly
Follow these steps for reliable results:
- Prepare: Rest for 5 minutes, avoid caffeine, and empty the bladder.
- Position: Sit upright with feet flat, back supported, and the cuff on bare skin at heart level.
- Arm Choice: Use the arm with the higher initial reading.
- Multiple Readings: Take 2–3 measurements, 1–2 minutes apart, and average them.
- Device Validation: Ensure oscillometric devices are clinically tested for accuracy.
Always measure while seated, rested, and with a validated blood pressure monitor. To ensure health safety and accurate readings Finicare Medical FC-BP25 Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitor is one of the best solutions. The device is known for its compactness and accuracy and is recommended by many doctors and health practitioners. Finicare Medical FC-BP25 is the best option out there.
6. Common Questions and Myths Debunked
Q1: Is the left arm more accurate for BP measurement?
A: No. While the left arm is closer to the heart, anatomical differences mean either arm can be used. Always follow guidelines to compare both arms initially.
Q2: What if my arms show different readings?
A: A difference of ≤10 mmHg is normal. Persistent IADs >10 mmHg may indicate arterial blockages and require medical evaluation.
Q3: Can wearable devices replace traditional cuffs?
A: PPG-based wearables show promise but require rigorous calibration and validation for clinical use.
Q4: Does arm position affect readings?
A: Yes. An arm positioned above or below heart level can alter systolic BP by 5–10 mmHg.
Q5: Should I use the same arm every time?
A: Yes. Consistency minimizes variability and improves trend analysis.
Q6: Can obesity affect arm choice?
A: Larger arms may require a bigger cuff. Use the arm that accommodates the cuff properly.
Q7: Are home monitors as accurate as clinic devices?
A: Yes, if validated by organizations like the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI).
Q8: Why do my readings vary throughout the day?
A: BP fluctuates with activity, stress, and circadian rhythms. Track trends rather than single measurements.
Q9: Can I measure BP on my wrist?
A: Wrist monitors are less accurate unless positioned precisely at heart level.
Q10: How do advanced algorithms improve accuracy?
A: Techniques like CWT and deep learning enhance signal analysis in PPG-based systems, reducing motion artifacts and improving classification accuracy.
Conclusion
Accurate blood pressure measurement hinges on proper technique, including arm selection. Always measure both arms initially, adhere to guidelines, and use validated devices. Emerging technologies like PPG and AI-driven algorithms may further refine accuracy, but user adherence to best practices remains irreplaceable. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers are key to managing cardiovascular health effectively.