What Are the Most Accurate Blood Pressure Monitors?
What Are the Most Accurate Blood Pressure Monitors?
Blood pressure monitoring is a crucial aspect of maintaining good health, especially for individuals with hypertension or those at risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. The accuracy of blood pressure monitors plays a vital role in providing reliable readings that can guide medical decisions and help manage overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the different types of blood pressure monitors available, factors that affect their accuracy, and recommend some of the most accurate options on the market.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
Mercury Sphygmomanometers
Mercury sphygmomanometers have long been considered the gold standard for blood pressure measurement in clinical settings. These devices work by using a mercury column to measure the pressure exerted by the blood against the arterial walls. The reading is obtained by listening to the Korotkoff sounds through a stethoscope while gradually releasing the pressure in the cuff.
Advantages:
- High accuracy: Mercury sphygmomanometers are known for their precise measurements, making them a reliable choice for healthcare professionals.
- Widely recognized: They have been used for decades and are familiar to most medical practitioners.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental concerns: Mercury is a toxic substance, and the disposal of mercury-containing devices poses a significant environmental risk.
- Skill required: Proper use of a mercury sphygmomanometer requires training and experience to accurately detect the Korotkoff sounds.
- Bulky and inconvenient: These devices are relatively large and not suitable for home use or portable monitoring.
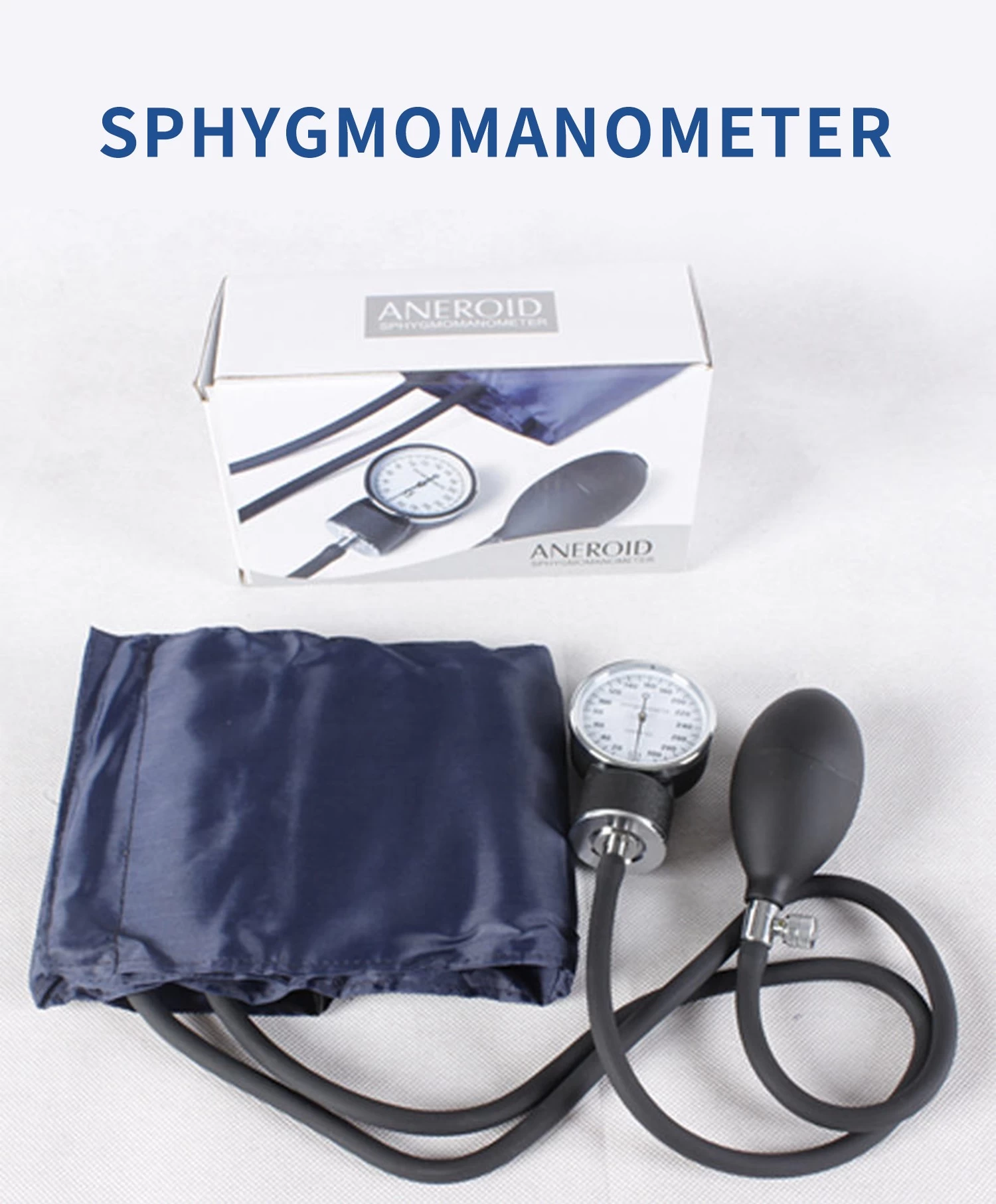
Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are another type of manual blood pressure monitor. Instead of using mercury, they employ a mechanical gauge to measure the pressure. The gauge is connected to a cuff that is inflated around the upper arm, and the reading is obtained by observing the position of the needle on the dial.
Advantages:
- Mercury-free: Aneroid sphygmomanometers eliminate the environmental concerns associated with mercury.
- Compact and portable: They are smaller and lighter than mercury sphygmomanometers, making them more convenient for home use and travel.
- Relatively accurate: When properly calibrated, aneroid sphygmomanometers can provide reliable readings.
Disadvantages:
- Calibration required: Aneroid sphygmomanometers need to be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurements. Over time, the mechanical components may become less precise.
- Skill-dependent: Similar to mercury sphygmomanometers, using an aneroid sphygmomanometer requires some skill to obtain accurate readings.
Electronic Blood Pressure Monitors
Electronic blood pressure monitors have gained popularity in recent years due to their ease of use and convenience. These devices use sensors to detect the pressure changes in the arterial walls and display the readings digitally. There are two main types of electronic blood pressure monitors: upper-arm and wrist monitors.
Upper-Arm Electronic Blood Pressure Monitors
Upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitors are considered the most accurate type of electronic monitor. They work by inflating a cuff around the upper arm and measuring the pressure using oscillometric technology. The device then calculates the systolic and diastolic blood pressure values based on the detected pressure waves.
Advantages:
- High accuracy: When used correctly, upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitors can provide readings that are comparable to those obtained with mercury sphygmomanometers.
- Easy to use: These monitors are designed to be user-friendly, with simple one-button operation and clear digital displays.
- Automatic inflation and deflation: The cuff inflates and deflates automatically, eliminating the need for manual adjustment.
- Memory functions: Many upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitors can store multiple readings, allowing users to track their blood pressure over time.
Disadvantages:
- Size and portability: Upper-arm monitors are larger than wrist monitors and may not be as convenient for on-the-go use.
- Cuff size matters: Using the wrong cuff size can lead to inaccurate readings, so it's important to choose the appropriate cuff size for the user's arm circumference.

Wrist Electronic Blood Pressure Monitors
Wrist electronic blood pressure monitors are a more compact and portable option. They work in a similar way to upper-arm monitors, but the cuff is worn around the wrist instead of the upper arm. Wrist monitors use oscillometric technology to measure the pressure and display the readings digitally.
Advantages:
- Compact and portable: Wrist monitors are small and lightweight, making them easy to carry around and use anywhere.
- Quick and convenient: They can be used without removing clothing, and the measurement process is relatively fast.
- Some models offer additional features: Such as wireless connectivity, which allows users to sync their readings with a smartphone or other device.
Disadvantages:
- Lower accuracy: Wrist monitors are generally less accurate than upper-arm monitors, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who are obese.
- Positioning is crucial: To obtain accurate readings, the wrist must be positioned at heart level, which can be challenging for some users.
- Cuff size and fit: Similar to upper-arm monitors, using the wrong cuff size or having a poor cuff fit can affect the accuracy of the readings.
Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Blood Pressure Monitors
User Technique
The way a blood pressure monitor is used can have a significant impact on the accuracy of the readings. Some common user errors include:
- Incorrect cuff placement: The cuff should be placed snugly around the upper arm or wrist, with the center of the cuff over the artery. If the cuff is too loose or too tight, it can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Improper arm position: The arm should be supported and relaxed, with the elbow at heart level. If the arm is elevated or dangling, it can affect the blood pressure measurement.
- Movement during measurement: Any movement, such as talking, moving the arm, or crossing the legs, can cause the readings to be inaccurate. It's important to remain still during the measurement process.
- Not following the manufacturer's instructions: Each blood pressure monitor has specific instructions for use, and it's essential to follow these instructions carefully to ensure accurate readings.
Cuff Size
Using the correct cuff size is crucial for obtaining accurate blood pressure readings. Cuffs that are too small can result in falsely elevated readings, while cuffs that are too large can lead to falsely low readings. The appropriate cuff size depends on the circumference of the upper arm or wrist. Most blood pressure monitors come with a range of cuff sizes, and it's important to select the size that fits the user's arm or wrist comfortably.
Calibration
Regular calibration of blood pressure monitors is essential to ensure their accuracy over time. Electronic blood pressure monitors, in particular, may require calibration periodically to account for any drift in the sensor readings. Some monitors have built-in calibration features, while others need to be calibrated by a healthcare professional or sent back to the manufacturer for calibration. It's important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for calibration frequency.
Environmental Factors
Certain environmental factors can also affect the accuracy of blood pressure monitors. For example, extreme temperatures, humidity, and electromagnetic interference can all impact the performance of the device. It's best to use blood pressure monitors in a stable environment, away from sources of heat, cold, moisture, and electromagnetic fields.
Recommended Accurate Blood Pressure Monitors
Omron Platinum Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitor
The Omron Platinum is a highly accurate upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitor that is widely recommended by healthcare professionals. It uses advanced IntelliSense technology to provide precise readings and features a large, easy-to-read display. The monitor also has a built-in memory that can store up to 100 readings, making it convenient for tracking blood pressure trends over time. Additionally, the Omron Platinum comes with a custom-fit cuff that ensures a comfortable and accurate fit for a wide range of arm sizes.
Withings BPM Connect
The Withings BPM Connect is another top-rated upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitor. It offers high accuracy and is compatible with both iOS and Android devices, allowing users to sync their readings with the Withings Health Mate app. The app provides detailed insights into blood pressure trends, offers personalized health tips, and can even share data with healthcare providers. The Withings BPM Connect also features a large, backlit display and an easy-to-use one-button operation.
Beurer BP55 Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitor
The Beurer BP55 is a reliable and accurate upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitor that is known for its user-friendly design. It has a large, clear display with extra-large digits, making it easy to read for individuals with visual impairments. The monitor also offers advanced features such as irregular heartbeat detection and a two-user memory function, allowing multiple family members to use the device. The Beurer BP55 comes with a comfortable, adjustable cuff that fits most arm sizes.
Omron M6 Comfort Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor
If you prefer a wrist blood pressure monitor, the Omron M6 Comfort is a popular choice. While wrist monitors are generally less accurate than upper-arm monitors, the Omron M6 Comfort is designed to provide reliable readings. It features a compact and lightweight design, making it convenient for on-the-go use. The monitor has a large, easy-to-read display and a one-touch operation. It also includes a memory function that can store up to 60 readings. However, it's important to note that wrist monitors may not be suitable for all individuals, especially those with certain medical conditions or who are obese.
Tips for Choosing and Using a Blood Pressure Monitor
Consider Your Needs
When choosing a blood pressure monitor, consider your specific needs and preferences. If you need a highly accurate monitor for medical purposes, an upper-arm electronic blood pressure monitor is likely the best option. However, if you value portability and convenience, a wrist monitor may be more suitable. Additionally, think about features such as memory functions, wireless connectivity, and ease of use.
Look for Certification
To ensure the accuracy of a blood pressure monitor, look for devices that have been certified by recognized organizations such as the American Heart Association (AHA), the European Society of Hypertension (ESH), or the British Hypertension Society (BHS). These certifications indicate that the monitor has undergone rigorous testing and meets certain standards of accuracy.
Read Reviews
Before purchasing a blood pressure monitor, read reviews from other users and healthcare professionals. This can give you an idea of the monitor's performance, reliability, and ease of use. Look for reviews that mention accuracy, as well as any potential issues or drawbacks.
Follow the Manufacturer's Instructions
Once you have chosen a blood pressure monitor, it's important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully for proper use and maintenance. This includes using the correct cuff size, positioning the arm or wrist correctly, and calibrating the monitor regularly. By following these instructions, you can ensure that you get the most accurate readings possible.
Measure at the Right Time
The time of day and other factors can affect blood pressure readings. It's generally recommended to measure blood pressure at the same time each day, preferably in the morning before eating or taking medication. Avoid measuring blood pressure immediately after exercise, smoking, or consuming caffeine. Also, make sure to rest for a few minutes before taking a reading to allow your blood pressure to stabilize.
Take Multiple Readings
To get a more accurate picture of your blood pressure, take multiple readings at each measurement session. Wait at least one minute between readings and record the average of the readings. This can help reduce the impact of any random fluctuations in blood pressure.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
If you have any concerns about your blood pressure or the accuracy of your blood pressure monitor, consult your healthcare provider. They can provide you with personalized advice and guidance on blood pressure monitoring and help you determine if any further testing or treatment is needed.
In conclusion, choosing an accurate blood pressure monitor is essential for maintaining good health and effectively managing blood pressure. While mercury sphygmomanometers have long been considered the gold standard, electronic blood pressure monitors, especially upper-arm models, offer high accuracy, ease of use, and convenience. By considering factors such as user technique, cuff size, calibration, and environmental conditions, and following the tips for choosing and using a blood pressure monitor, you can ensure that you get reliable readings that can help you make informed decisions about your health. Remember to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance on blood pressure monitoring.