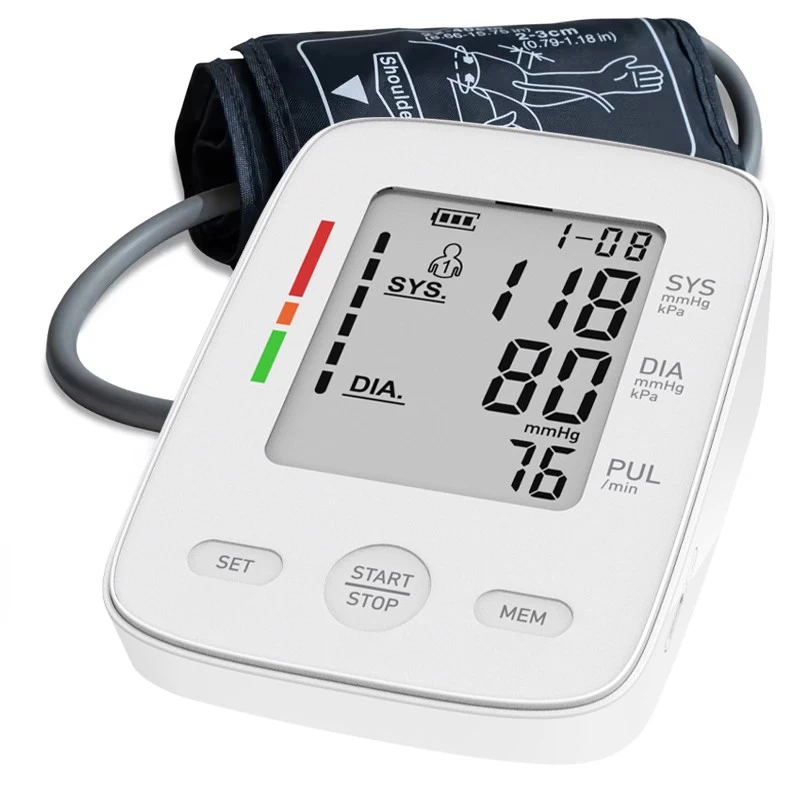
Tips for Using a Blood Pressure Monitor
Gentle monitoring: How to use a blood pressure monitor correctly
Blood pressure is an important indicator of physical health, especially in modern fast-paced life, many people face blood pressure problems due to poor diet, work pressure or genetic factors. For this reason, mastering the correct blood pressure monitoring method has become a skill that everyone should have. And a blood pressure monitor is a gentle guardian in our daily health management.
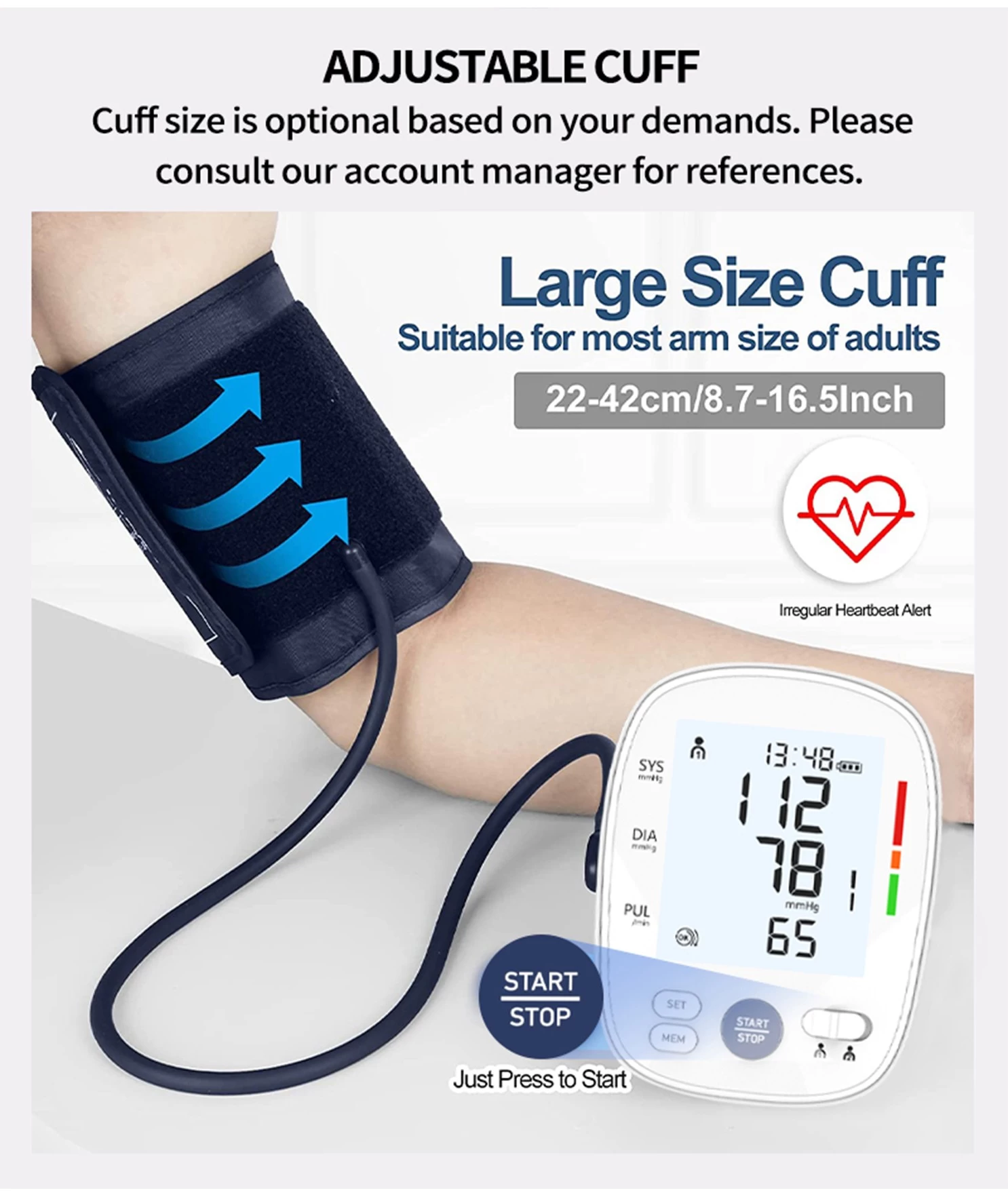
Chapter 1: Choose a suitable blood pressure monitor
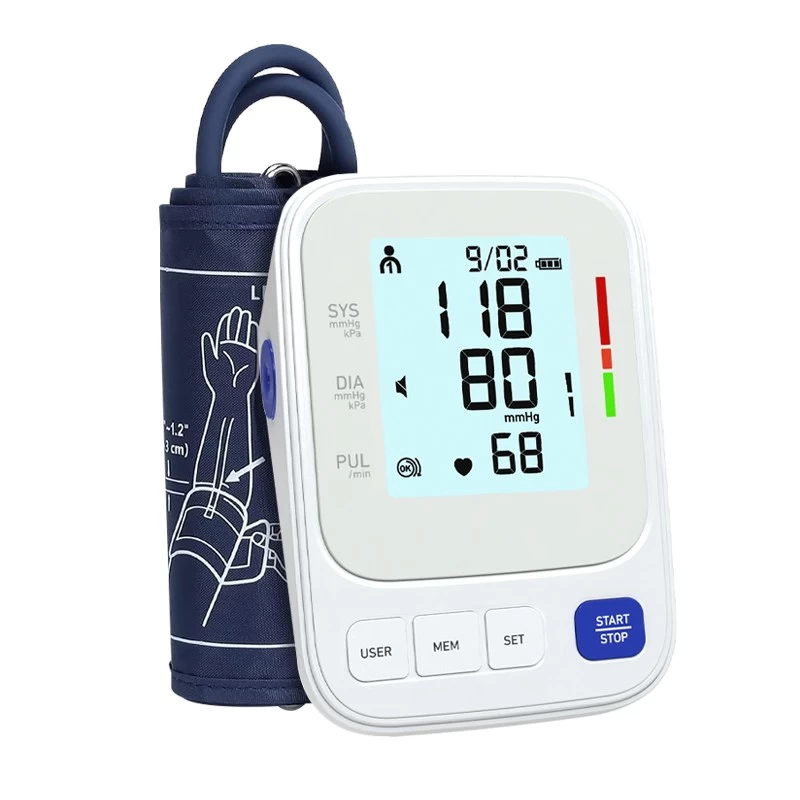
There are different types of blood pressure monitors, the most common ones are upper arm, wrist and finger types. For most people, an upper arm blood pressure monitor is the most accurate choice. Although wrist or finger types are more convenient, they may be affected by wrist posture and device position during measurement, and the data may be biased. Therefore, it is recommended to choose a quality-guaranteed upper arm blood pressure monitor and make sure it has a cuff that fits your arm size.
Chapter 2: Correct measurement posture
In order to obtain accurate blood pressure data, posture is crucial. First, sit down and relax your body. Your feet should be flat on the ground, with your knees and ankles naturally bent. Fix the blood pressure monitor cuff on your upper arm, and the cuff position should be about 1-2 cm above your elbow. Make sure your upper arm is stable and parallel to your heart, and avoid crossing your arms or raising your upper arms.
During the measurement, stay quiet, do not talk or move, and avoid any distractions. If possible, it is best to measure at the same time every day to help you understand the fluctuation pattern of blood pressure.
Chapter 3: How to interpret blood pressure data
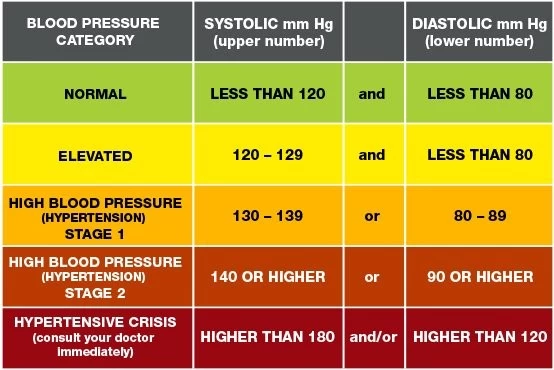
Blood pressure consists of two numbers, systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the pressure exerted by blood on the blood vessel wall when the heart contracts, while diastolic pressure is the pressure when the heart relaxes.
Ideal blood pressure: less than 120/80 mmHg
Normal blood pressure: 120-129/80-84 mmHg
Prehypertension: 130-139/85-89 mmHg
Hypertension: ≥140/90 mmHg
If you find that your blood pressure is continuously high, it is recommended to consult a doctor in time. Remember that the results of a single measurement may fluctuate, so you need to monitor it continuously and record the data to make an accurate judgment.
Chapter 4: Precautions and Health Tips
Regular monitoring: Even if you do not have obvious symptoms of high blood pressure, you should measure your blood pressure regularly to understand your health status. Especially those with a family history of high blood pressure or those with high life pressure need more attention.
Don't over-measure: Although blood pressure monitoring is part of health management, excessive attention to changes in blood pressure may cause anxiety. Keep a calm mind, and the frequency and timing of monitoring should be reasonably arranged according to personal health status.
Lifestyle adjustment: A reasonable diet, moderate exercise, reduced salt intake, and maintaining a healthy weight can all help regulate blood pressure. Combined with blood pressure monitoring, a good health management cycle is formed.
This article aims to remind everyone that blood pressure monitoring is not only a tool to understand physical health, but also a daily care and ritual. Through precise monitoring, we can maintain a more peaceful and warm dialogue with our bodies, perceive its changes and make timely adjustments.