Mastering the Use of a Blood Pressure Monitor
Precise control: A complete guide to using a blood pressure monitor
Blood pressure is a key indicator of heart health. It can help us understand the health of our blood vessels and detect potential health problems early. Whether you are new to blood pressure monitors or are already accustomed to daily measurements, it is crucial to master the correct use method. This article will take you into the world of blood pressure monitoring, from choosing the right device to the correct operating steps, so that you can easily master the use of this health tool.

Chapter 1: Choose the right blood pressure monitor
There are many types of blood pressure monitors on the market. When choosing, you should decide according to your needs. The two most common types are:
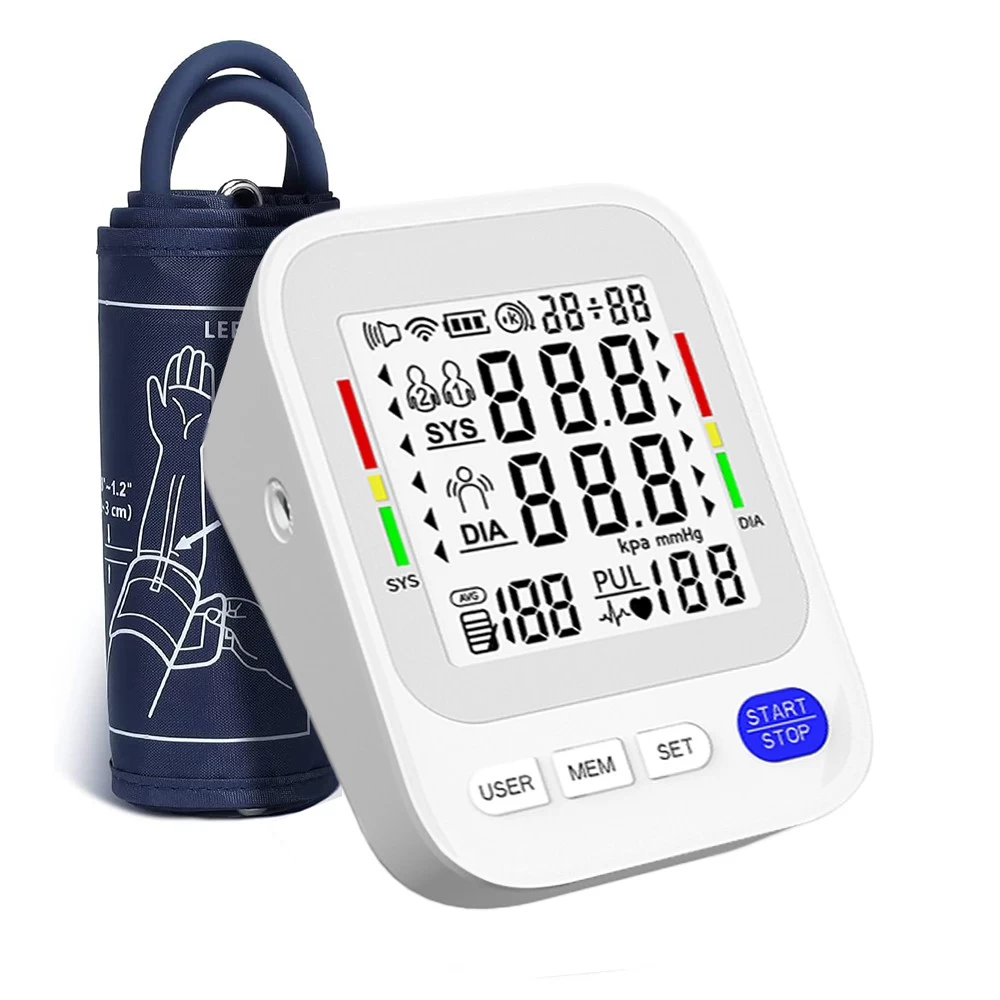
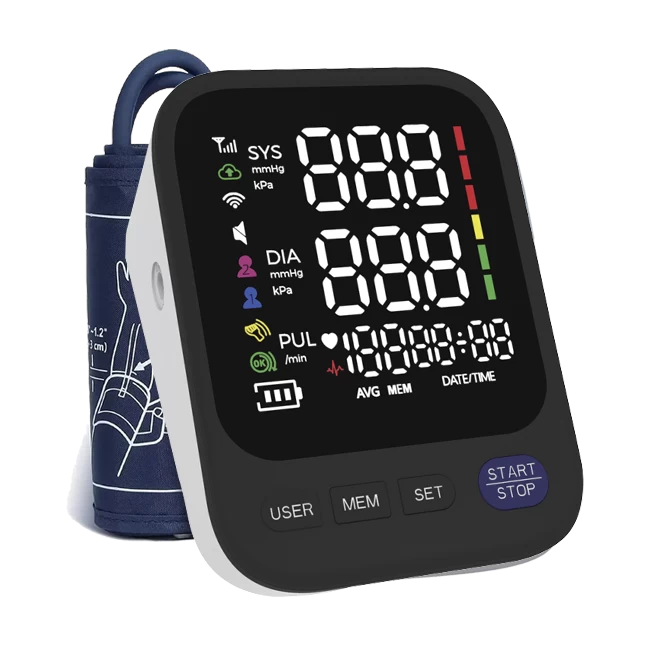
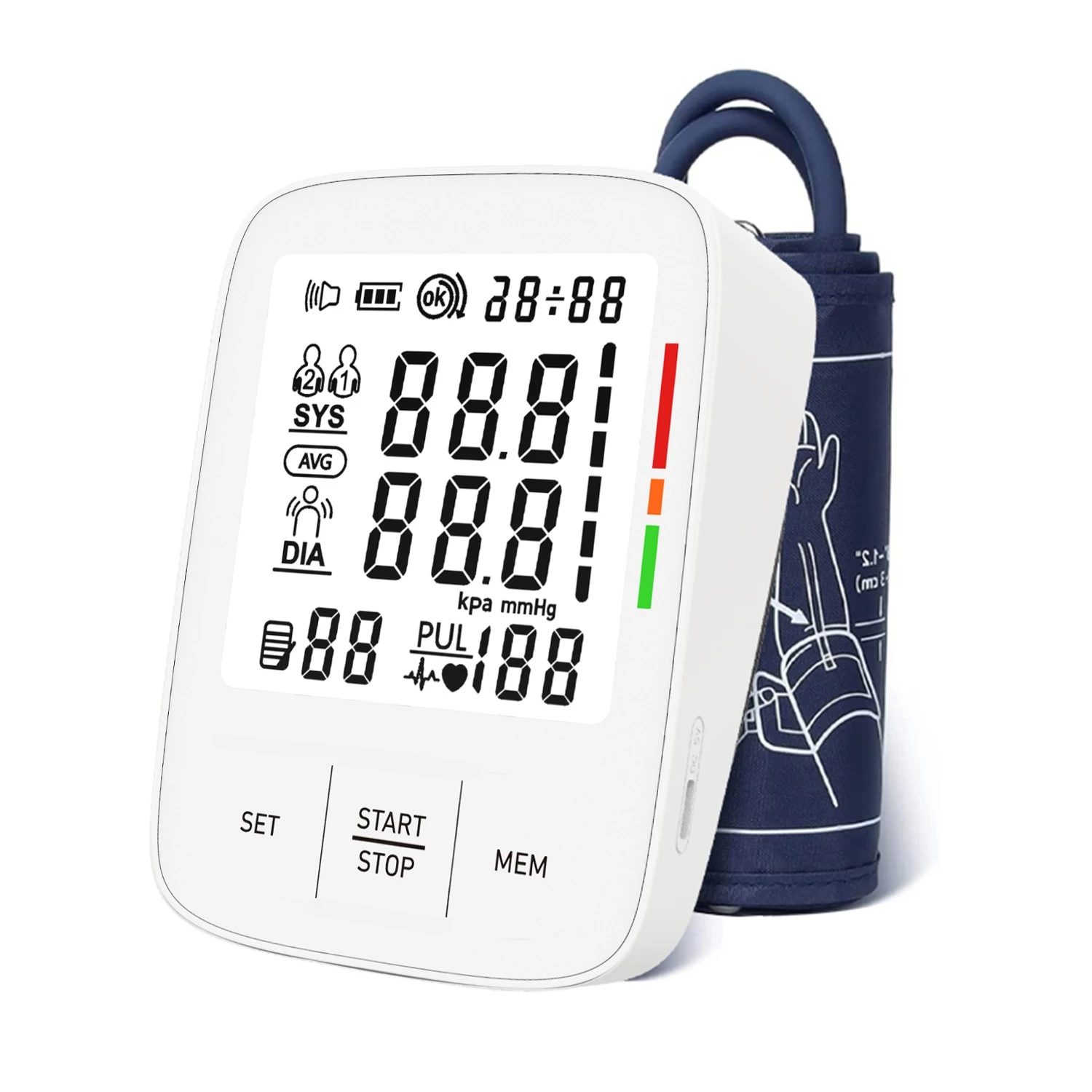
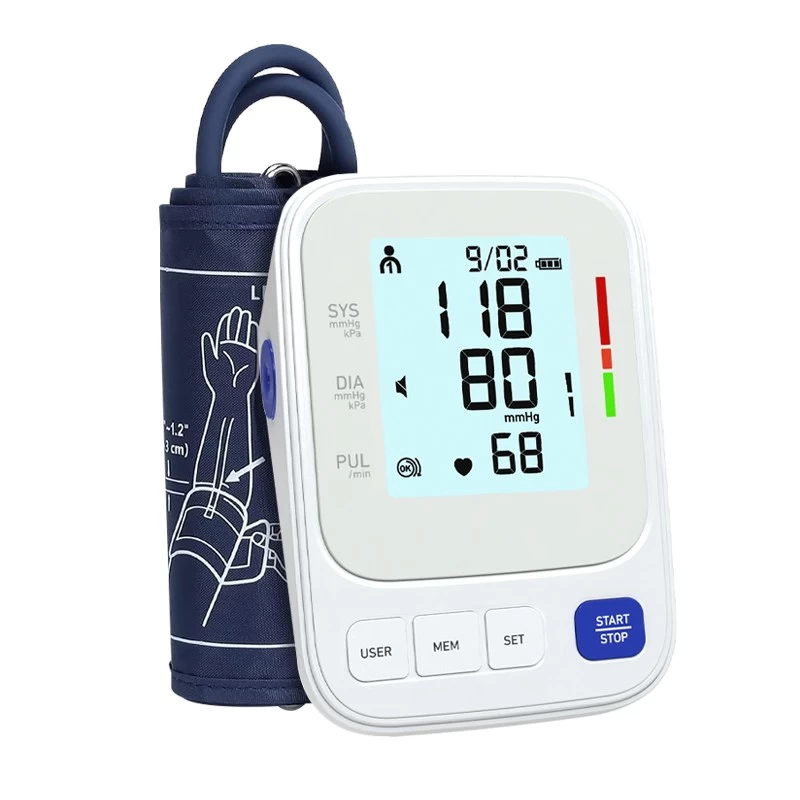
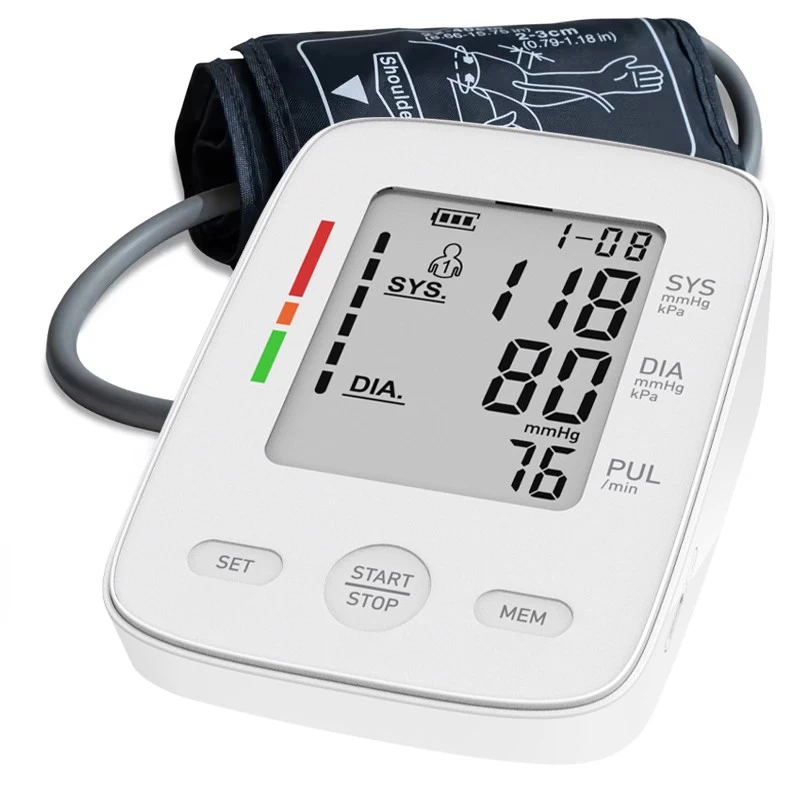
Upper arm blood pressure monitor: This type of blood pressure monitor has high accuracy and is suitable for most users. When measuring, the cuff is wrapped around the upper arm, and the measurement results are relatively stable. It is the standard type recommended by the medical community.
Wrist blood pressure monitor: This device is easy to carry and is suitable for users who often go out or have limited space. However, since the measurement is greatly affected by the position of the wrist, it may cause deviations, so it is not as accurate as an upper arm blood pressure monitor.
When choosing, make sure the device is suitable for your needs, especially the size of the cuff. Don't buy cheap and inaccurate brands. After all, health is priceless.
Chapter 2: Correct Measurement Posture
Even with accurate equipment, improper measurement posture may affect the accuracy of the results. To ensure the most reliable results for each measurement, please pay attention to the following points:
Stay relaxed: Before measuring, sit down, take a few deep breaths, and relax your body. Avoid strenuous exercise or drinking coffee before measuring.
Correct sitting posture: Sit up straight, put your feet naturally on the ground, and do not cross your knees. The arms should be relaxed and the elbows should be parallel to the heart.
Cuff position: Put the cuff on the upper arm, the position should be 1-2 cm above the elbow, and make sure the cuff is close to the skin, but not too tight.
Avoid talking and moving: During the measurement, stay silent and stable, and avoid talking, talking or changing body position, which will affect the measurement results.
Chapter 3: How to interpret blood pressure results
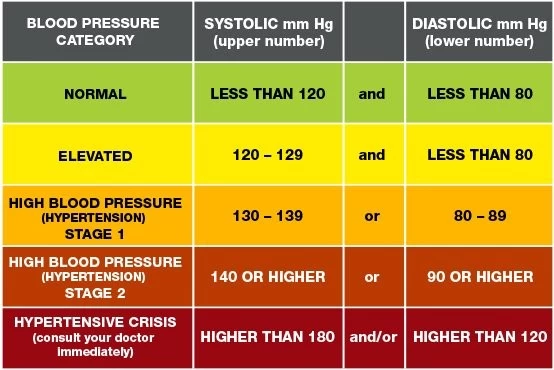
The normal range of blood pressure is divided into several levels. Understanding these data is the key to monitoring blood pressure:
Ideal blood pressure: systolic pressure less than 120, diastolic pressure less than 80 (120/80 mmHg)
Normal blood pressure: systolic pressure 120-129, diastolic pressure 80-84 (120-129/80-84 mmHg)
Prehypertension: systolic pressure 130-139, diastolic pressure 85-89 (130-139/85-89 mmHg)
Hypertension: systolic pressure ≥140, diastolic pressure ≥90 (≥140/90 mmHg)
If your blood pressure exceeds the normal range, especially when the continuous measurement results are high, you should consult a doctor in time to avoid delaying treatment.
Chapter 4: Precautions and health tips
Regular monitoring: Even if there are no obvious health problems, it is recommended to monitor blood pressure regularly. Fluctuations in blood pressure may reflect changes in lifestyle, mood and other factors.
Avoid excessive anxiety: If the result of a measurement is not ideal, there is no need to be overly anxious. Blood pressure is affected by many factors, and a single measurement does not represent a comprehensive health status.
Record data: Record blood pressure values after each measurement, including the measurement time, date, and feeling state. This helps doctors assess your health trends.
Healthy lifestyle: A reasonable diet, increased exercise, maintaining a suitable weight, reducing high-salt diets and excessive caffeine intake, these lifestyles can effectively help control blood pressure.
Avoid self-diagnosis: If you suspect that you have high blood pressure and other problems, do not judge on your own, you should seek the advice of a professional doctor to ensure the timeliness and effectiveness of treatment.
Conclusion: Accurate monitoring, guarding health:
Mastering the correct blood pressure monitoring skills is not only a way to understand your own health, but also a daily ritual to protect your body. Each measurement is not just for a number, but a dialogue with your body, allowing us to better care for ourselves, manage our health, and live more calmly and balanced.