How to Read a Hospital Monitor?
A hospital monitor is a device used to keep track of a patient’s health in real-time. It measures vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and sometimes oxygen levels. The monitor displays this information on a screen, allowing doctors and nurses to see how well a patient is doing.
It helps medical staff detect any problems quickly and take action if needed. Some monitors can also record data over time, which allows for observing trends in a patient’s condition. Hospital monitors are essential for continuous care, especially for critically ill patients or those undergoing surgery.
Table of Contents
1.How to read a hospital monitor?
2.What do the different colors on a hospital monitor indicate?
3.How does a hospital monitor measure heart rate?
4.What is the normal range for oxygen saturation on a hospital monitor?
5.What is the purpose of an ECG on a hospital monitor?
6.How can you reset a hospital monitor?
7.What are the common issues with hospital monitors?

1.How to read a hospital monitor?
By understanding the basics of a hospital monitor, you can interpret the data from a hospital monitor and stay informed about a patient’s health.
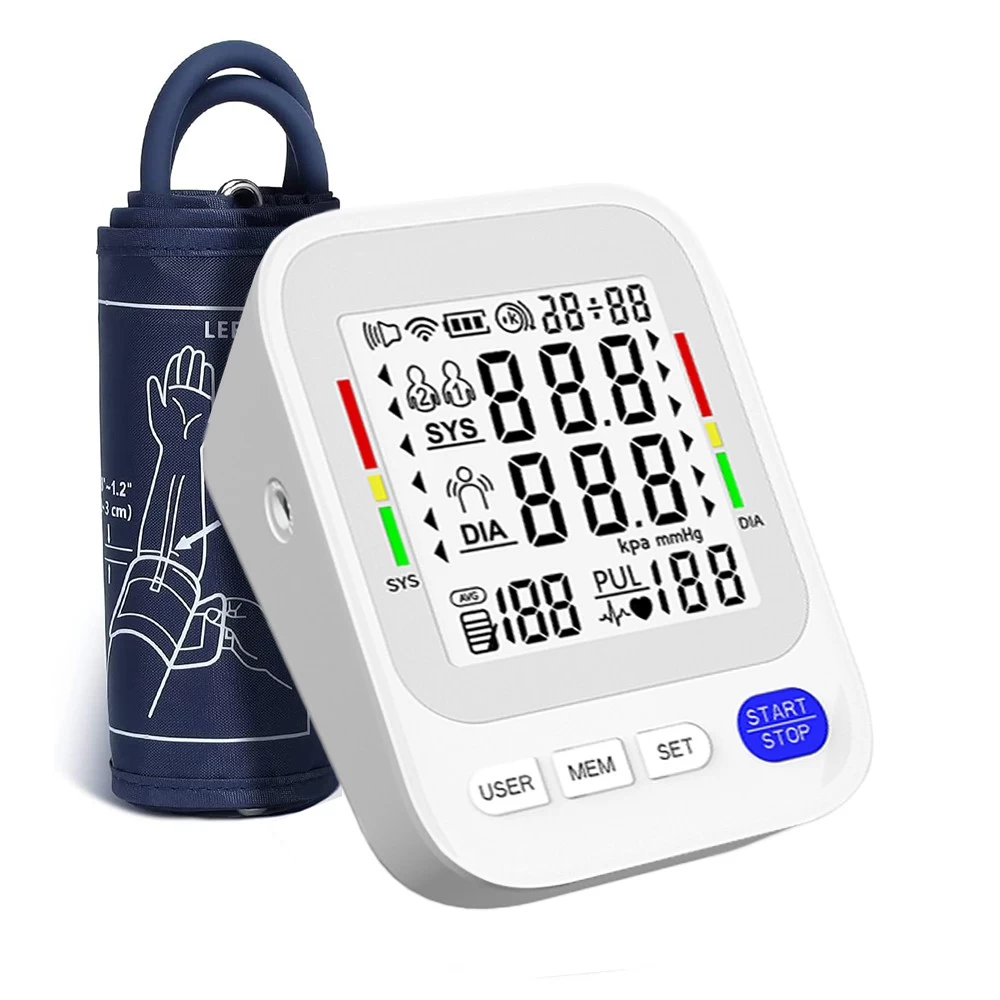
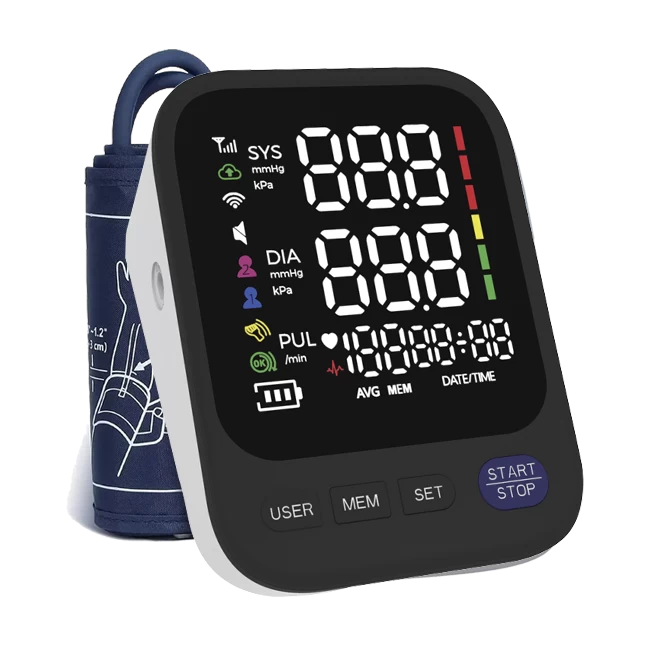
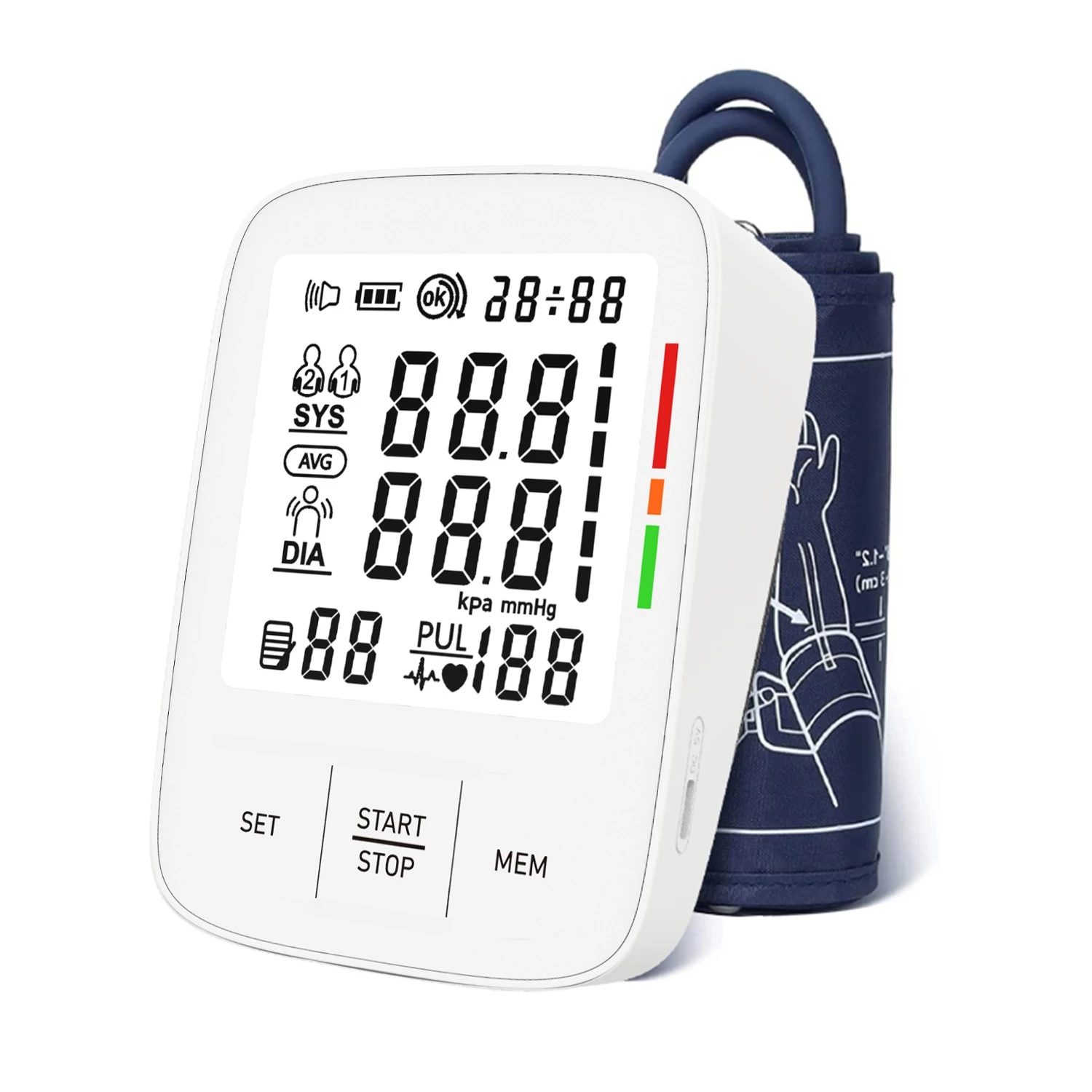
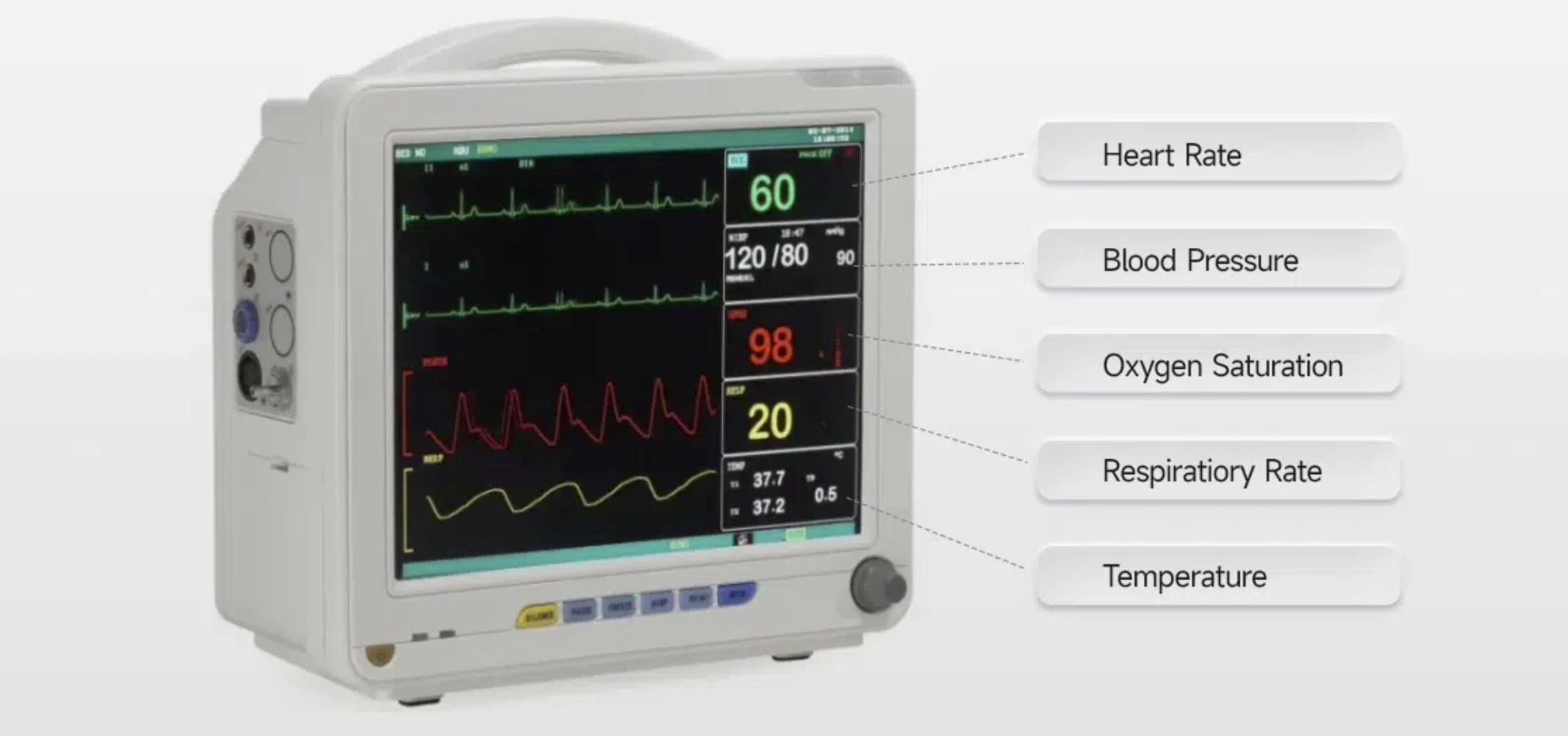
A hospital monitor shows vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. The main screen displays these measurements with numbers and graphs. For example, heart rate is usually shown as beats per minute (bpm), while blood pressure is displayed with two numbers: systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number).
1. Heart Rate
To read heart rate, look at the number on the screen, often next to a heart icon. This number shows how many times the heart beats in one minute. A normal heart rate for adults is typically between 60 and 100 bpm.
2. Blood Pressure
Blood pressure readings appear as two numbers, such as 120/80 mmHg. The first number (systolic) measures the pressure when the heart beats, and the second number (diastolic) measures the pressure when the heart rests between beats. Normal blood pressure is generally around 120/80 mmHg.
Finicare Medical, along with the professional 24-hour BPM manufacturer, tracks, analyzes, and manages data, providing critical insights to decrease the risk of cardiovascular events. learn more: https://www.medicaldevicessuppliers.com/category/Blood-Pressure-Monitor.html
3. Oxygen Levels
Oxygen levels are shown as a percentage, often next to a pulse oximeter icon. This percentage indicates how much oxygen is in the blood. Normal levels are usually between 95% and 100%.
4. Respiratory
To read a hospital monitor for respiratory rate, look at the number labeled “Resp Rate” or similar. It shows how many breaths per minute. Standard rates for adults are usually 12-20 breaths per minute.
5. Temperature
For temperature, find the “Temp” reading. It shows body temperature in degrees, usually Celsius or Fahrenheit. Normal body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C). If the readings are high or low, alert a healthcare provider.
If the monitor sounds an alarm or shows a warning, there may be an issue with one of the vital signs. Check the readings carefully and follow any instructions provided by medical staff.
2.What do the different colors on a hospital monitor indicate?
On a hospital monitor, different colors are used to help healthcare providers quickly identify essential information. Each color typically represents a specific type of vital sign or function:
1. Green
This color usually represents the ECG (electrocardiogram) or heart rate. It shows the heart’s electrical activity, helping to monitor heart rhythms.
2. Yellow or Amber
It is often used to indicate the respiratory rate or breathing patterns. It helps track how fast or slow a patient is breathing.
3. Blue or Cyan
This color is often used for oxygen saturation (SpO2) levels. It shows how well oxygen is being carried in the blood.
4. Red
Red signals critical values, such as alarms for dangerously high or low heart rates, blood pressure, or oxygen levels. It alerts staff to take immediate action.
5. White
This color is often used for additional readings like temperature or secondary waveforms. These colors help doctors and nurses quickly understand a patient’s condition at a glance, allowing them to respond faster in emergencies.
3.How does a hospital monitor measure heart rate?
A hospital monitor measures heart rate by using sensors that detect the electrical signals produced by the heart. These sensors are often placed on the patient’s chest using sticky patches called electrodes. When the heart beats, it generates electrical impulses that travel through the body. The electrodes pick up these impulses and send them to the monitor.
The monitor then processes the signals and calculates the number of heartbeats per minute, which is displayed on the screen as the heart rate. The heart rate is usually shown as a number, such as 75 beats per minute (bpm), and may also be displayed on a waveform graph.
Some monitors use a technique called pulse oximetry, which measures the changes in blood volume with each heartbeat using a sensor placed on a finger or earlobe. This method also helps estimate heart rate by detecting the rhythmic flow of blood.
In both cases, the hospital monitor provides real-time information about the heart rate, which is crucial for assessing a patient’s health and making necessary medical decisions.
4.What is the normal range for oxygen saturation on a hospital monitor?
The normal range for oxygen saturation (SpO2) on a hospital monitor is usually between 95% and 100%. This percentage shows how much oxygen your blood carries compared to its total capacity.
When the SpO2 reading is in this range, your body gets enough oxygen, which is important for your organs and tissues to work well. If the oxygen saturation falls below 90%, it’s considered low, called hypoxemia. This can indicate breathing problems, lung issues, or other medical conditions.
In such cases, doctors may provide extra oxygen or other treatments. Monitoring SpO2, especially for respiratory or heart problems patients, is important to ensure they get enough oxygen to stay healthy.
5.What is the purpose of an ECG on a hospital monitor?
An ECG (electrocardiogram) on a hospital monitor checks the heart’s electrical activity. It shows how the heart beats and can help doctors spot irregular heartbeats, arrhythmias, heart attacks, or other heart conditions.
The ECG on a monitor displays the heart’s rhythm as waveforms on the screen, representing the electrical signals that make the heart muscles contract and pump blood. By looking at these waveforms, healthcare providers can tell if the heart is beating too fast, slow, or irregularly.
It also shows if there is any damage to the heart muscle, issues with the heart’s chambers, or if the heart is under strain. Using ECG monitoring, doctors and nurses can quickly respond to any dangerous changes in the heart’s activity, making it an important tool for hospital patient care.
6.How can you reset a hospital monitor?
Resetting a hospital monitor can help fix minor issues or clear alarms. Here’s a simple way to reset it
1. Check the Screen
Look for a reset button on the screen or the monitor’s main menu. Sometimes, it might be labeled as “Reset,” “Restart,” or “Reboot.”
2. Use the Power Button
If the screen has no reset option, try turning the monitor off using the power button. Please wait a few seconds, then turn it back on.
3. Unplug and Reconnect
If the monitor doesn’t have a power button, you can unplug it from the power source, wait a few seconds, and plug it back in.
4. Follow Manufacturer Instructions
Always check the user manual for specific reset instructions; different models may have other steps.
7.What are the common issues with hospital monitors?
Common issues with hospital monitors can include:
1. Loose or Disconnected Cables
Wires connecting the patient to the monitor can become loose or disconnected, causing the monitor to stop reading vital signs accurately.
2. Sensor Problems
Sensors, like those for ECG or SpO2, might not work correctly if placed incorrectly or if there is too much movement, leading to inaccurate readings.
3. Alarm Fatigue
Frequent or unnecessary alarms can overwhelm staff, causing them to miss important alerts.
4. Battery or Power Issues
Portable monitors might have low battery life, or stationary monitors may lose power if not plugged in correctly.
5. Software Glitches
Monitors may freeze or malfunction due to software issues, requiring a reset or technical support.
6. Calibration Errors
If the monitor is not calibrated correctly, the readings may be off, leading to incorrect patient data.
Regular maintenance and checks can help prevent these issues.
Reading a hospital monitor involves understanding the different lines, numbers, and alarms that display a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, oxygen levels, blood pressure, and breathing rate.
Knowing what each color and number means helps healthcare providers assess a patient’s condition quickly. Paying attention to alarms and looking for normal ranges ensures that any patient health changes are noticed and addressed promptly.